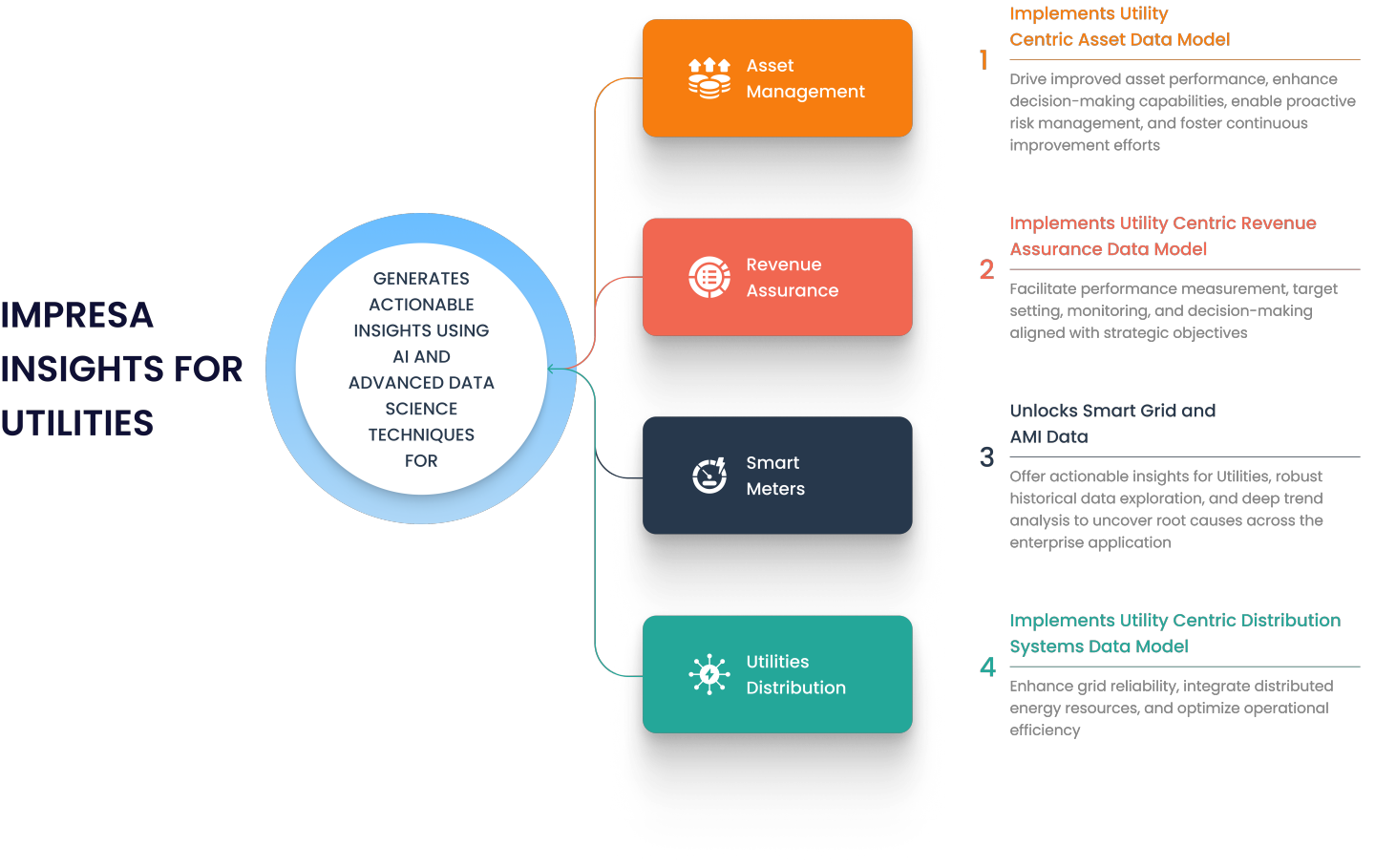
Impresa Insights
Flexible, Utility Centric Data Lakehouse and AI Platform to Drive Direct Business Outcomes.

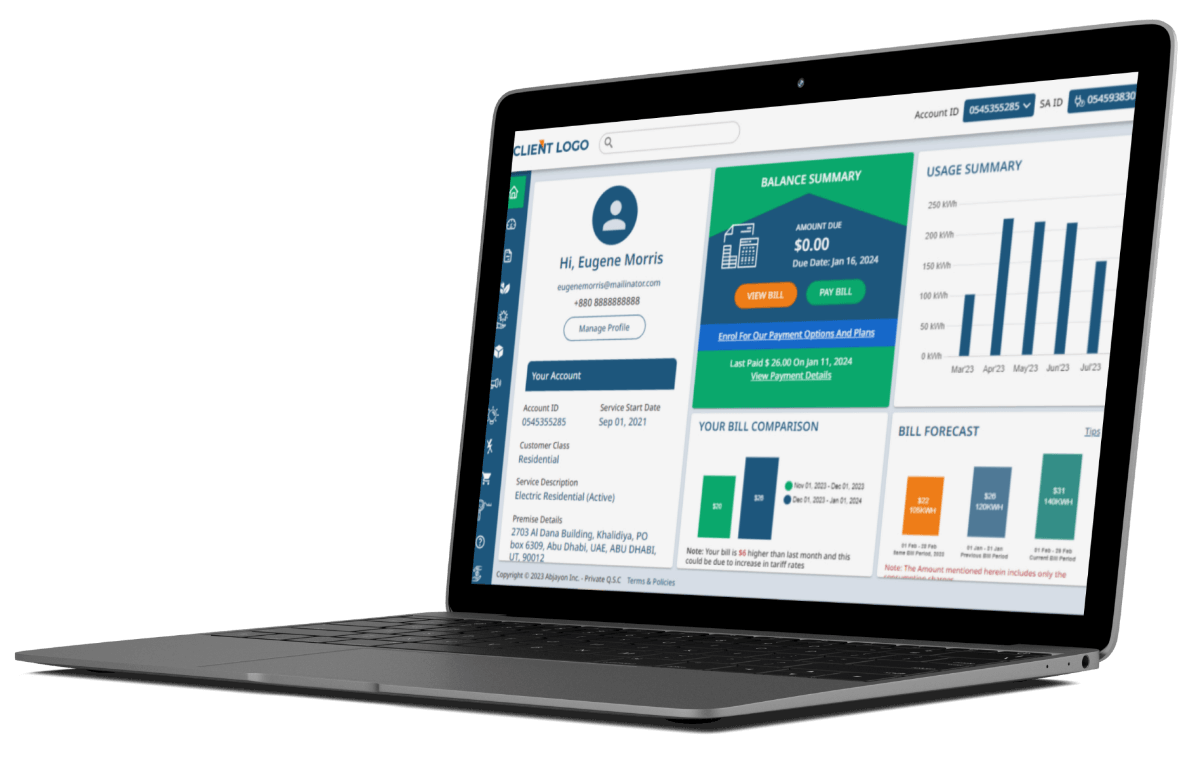
Presenting Impresa Insights
Abjayon presents Impresa Insights, a modular, scalable, and future-proof AI/ML-enabled big data enterprise platform for managing and analyzing the vast volumes of data in the Utility Industry.
Impresa Insights can help Master your Data
- Convert your Unstructured Data to meaningful analysis and insights in real-time.
- Combining back-office analytics and distributed analytics on a multi-solution platform.
- Monetize your Data and use it to develop new energy services, distribute resources efficiently, adapt infrastructures, and sustainably engage customers.
Utility Specific Data Lake
- Ability to connect with multiple data sources
- Built-in ML and data mining capabilities
- Built-in Self Service BI module
- Prebuilt storyboards and reports
- Ability to connect with multiple data sources
Impresa solutions
Energy Disaggregation
The energy disaggregation feature uses advanced AI/ML techniques to break down a consumer’s total energy consumption into the individual contributions of various appliance categories or devices.
- Automated energy disaggregation of energy consumption into appliance level consumption.
- State of Art model considers demographic, geographic, economic and climatic conditions.
- Modern UX for displaying action energy saving tips and relevant data for consumers using widgets.
- These reports can be published as widgets in customer portals or mobile app.
- Helps with grid resiliency and demand side management programs.
- Helps utility monetize the energy consumption data.
Value for Consumers
- Understand energy usage patterns. Detect unhealthy appliances.
- Use the information to make informed decisions about energy-saving opportunities.
Key Features
Non-Intrusive Monitoring is a method of analyzing and measuring energy consumption without the need for direct physical access or installation of sensors on individual devices. In the context of energy disaggregation, non-intrusive monitoring refers to the ability to track the usage of multiple appliances or electrical loads from a single measurement point, such as a smart meter or a centralized power monitoring system.
Here’s a more detailed explanation of Non-Intrusive Monitoring and how it works :
Single Measurement Point : Non-intrusive monitoring relies on data collected from a single point, usually where the electricity enters a building (e.g., the main circuit breaker or smart meter). The system monitors the overall energy consumption rather than measuring the consumption of each individual device separately.
Electrical Signature Recognition : Every appliance has a unique electrical signature that is reflected in how it draws power (e.g., current spikes, voltage drops, on/off patterns). Non-intrusive monitoring uses algorithms to recognize these patterns in the overall power data, allowing it to infer which appliances are being used and how much energy they are consuming.
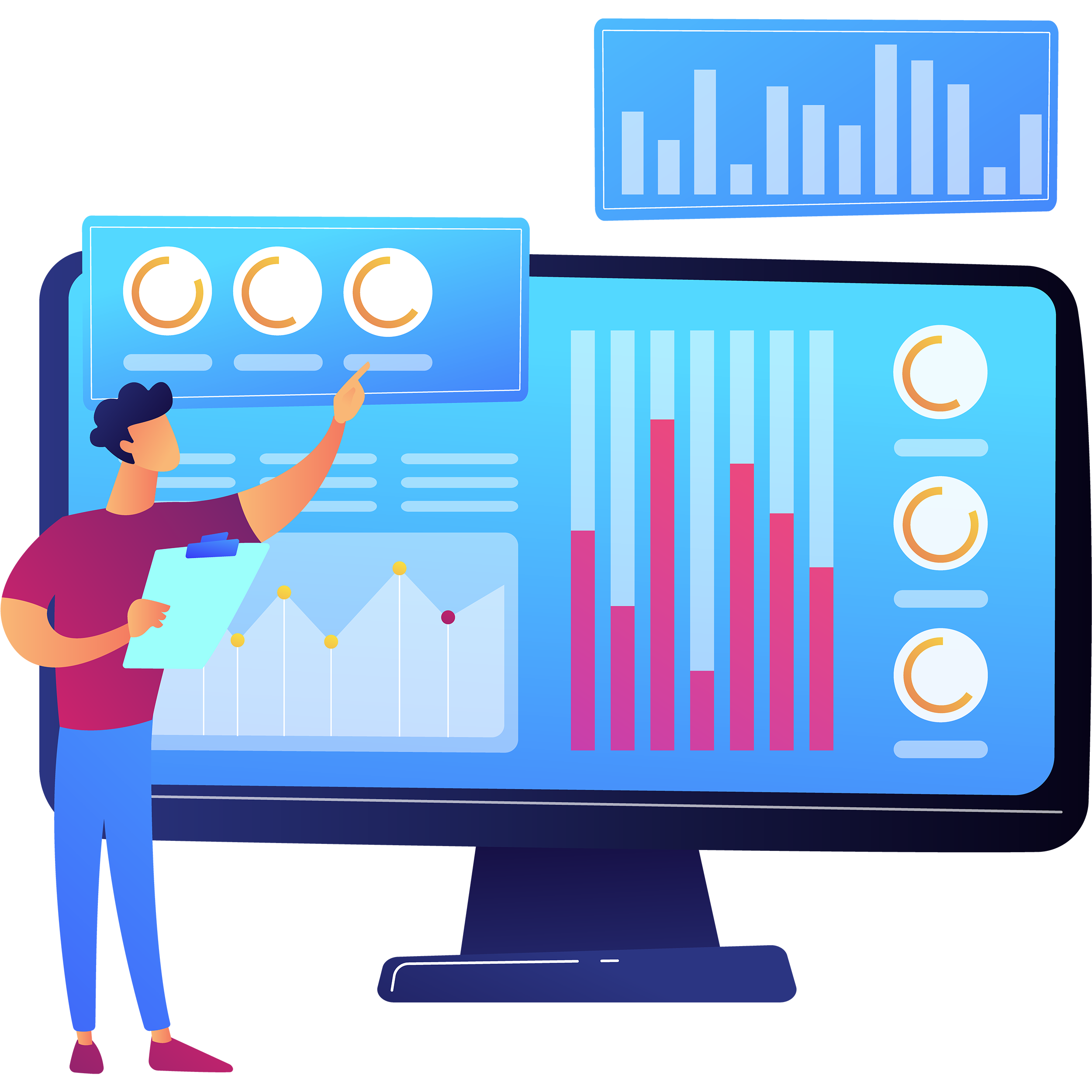

Appliance-Level Breakdown : Energy disaggregation provides a detailed breakdown of how much energy each appliance or device is using. By analyzing this data, users can identify which appliances are consuming the most energy and focus on optimizing or replacing those to reduce overall consumption. For example, if a refrigerator uses more energy than expected, it may indicate inefficiency, prompting maintenance or replacement with a more energy-efficient model.
Identifying Energy-Hungry Devices : Not all appliances are equally efficient, and energy disaggregation helps pinpoint which devices are consuming more power than they should. Energy-hungry devices like old HVAC systems, water heaters, or inefficient lighting systems are prime candidates for upgrades. Insights can show how these devices contribute to high energy bills and suggest alternatives like LED lights or more energy-efficient air conditioners.

Types of Faults Detected :
1. Increased Energy Consumption: An appliance may begin consuming more energy than it should, which could be due to mechanical wear, inefficient components (e.g., a worn-out motor), or internal faults.
2. Decreased Efficiency: If an appliance is using energy but not performing its function efficiently (e.g., an air conditioner running constantly but failing to cool), this could indicate a problem.
3. Continuous or Irregular Operation: An appliance that operates continuously without cycling off (e.g., a refrigerator compressor running nonstop) or turns on and off at irregular intervals may have a fault.
4. Failure to Operate: A device that draws no power when expected to be running might signal a failure or disconnect.
Here’s a breakdown of how energy disaggregation integrates with smart grids :
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) : Smart grids rely on AMI, which includes smart meters capable of sending and receiving data in real time. These meters not only measure overall consumption but, when integrated with energy disaggregation, can also break it down into specific appliance-level usage.
Automation and Control : Smart grids incorporate automated systems to monitor electricity flow, detect issues, and optimize energy distribution. This helps reduce outages, enhance grid reliability, and improve energy efficiency.
Benefits

Identification of Standby Power Consumption
Energy disaggregation can identify which appliances are drawing power unnecessarily, allowing users to take corrective actions like unplugging devices or using smart plugs to eliminate standby consumption.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Energy disaggregation helps users identify energy-hungry or inefficient devices. This data allows consumers to make targeted improvements, such as replacing outdated appliances, adjusting usage habits, or implementing energy-saving measures to reduce overall energy consumption.

Customized Energy-Saving
Many energy disaggregation systems provide personalized recommendations for reducing energy consumption based on each user’s unique usage patterns. These tailored suggestions can include replacing inefficient devices, adjusting usage schedules, or upgrading insulation, leading to more effective energy savings.
for Utilities





